فهرست طویلترین رودهای ایالات متحده آمریکا (بر پایه سرچشمه اصلی)
فهرست طویلترین رودهای ایالات متحده (انگلیسی: List of longest rivers of the United States)
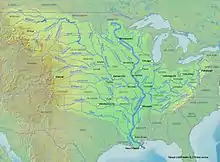
جدول
منبع اصلی for watershed و discharge data در جدول زیر رودهای آمریکای شمالی است. Conflicting data from other sources, if the difference is بزرگتر ۱۰ درصد، is reported in the notes. Discharge refers to the flow at the mouth.[n 1] در ستون "ایالتها، استانها، و تصاویر" , superscripts "s" و "m" "سرچشمه" و "مدخل". Non-U.S. states appear in italics. بجز در ستون "ایالتها, استانها, و تصاویر" , اختصارات به شرح زیر است: "km" برای "کیلومتر", "mi" بجای "مایل", "s" بجای "دقیقه", "m" بجای "متر", و "ft" بجای "foot". رودخانه است به طور کامل در داخل ایالات متحده نمی
| Key | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
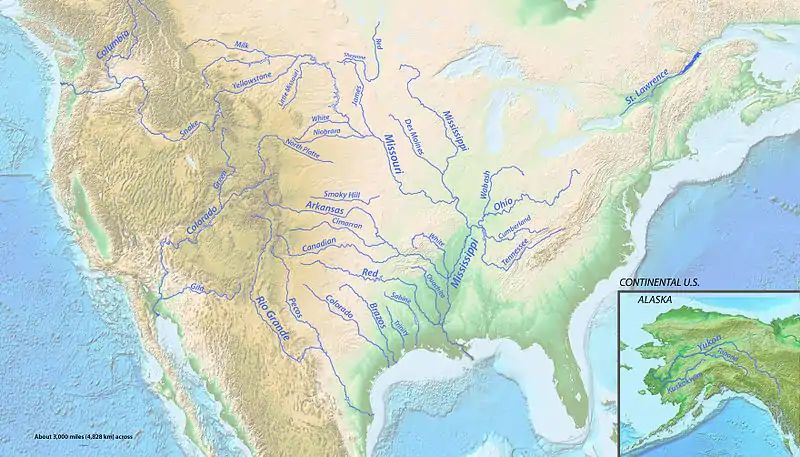
منابع
- Benke and Cushing, p. 527
- The Road Atlas. Chicago, Illinois: Rand McNally & Company. 2008. ISBN 0-528-93961-0.
- The mouth coordinates and source coordinates are from the Geographic Names Information System (United States Geological Survey) or the Canadian Geographical Names Data Base except for the coordinates of the mouth of the Colorado River، derived by geolocating with Google Earth.
- From Rivers of North America (ed. Benke and Cushing) unless otherwise noted.
- Benke and Cushing, p. 432
- "رود میزوری". Geographic Names Information System (GNIS). United States Geological Survey. October 24, 1980. Retrieved February 4, 2011.
- Benke and Cushing, p. 469
- "Rivers". The Atlas of Canada. Natural Resources Canada. Retrieved February 11, 2011.
- "Missouri River Basin basic geography and natural features". United States Geological Survey. Archived from the original on 7 April 2014. Retrieved February 20, 2011.
- Kammerer, J.C. (September 1, 2005). "Largest Rivers in the United States". United States Geological Survey. Retrieved January 22, 2011.
- Benke and Cushing, pp. 237, 331
- "رود میسیسیپی". Geographic Names Information System (GNIS). United States Geological Survey. June 4, 1980. Retrieved February 4, 2011.
- Benke and Cushing, p. 272
- "Atlin Lake (B.C.)". Natural Resources Canada. Archived from the original on 6 July 2011. Retrieved February 4, 2011.
- "رود یوکون". Geographic Names Information System (GNIS). United States Geological Survey. March 31, 1981. Retrieved February 4, 2011.
- Benke and Cushing, p. 796
- Benke and Cushing, p. 186
- Patino, Carlos; McKinney, Daene C.; Maidment, David R. "Water Management Information System for the رود ریوگرانده/Bravo Basin" Check
|url=value (help). University of تگزاس Center for Research in Water Resources. Retrieved February 19, 2011. - "رود ریوگرانده". Geographic Names Information System (GNIS). United States Geological Survey. March 30, 1979. Retrieved February 4, 2011.
- Benke and Cushing, p. 220
- Anderson, D. Larry (May 2002). "Utah's Perspective: The رودخانه کلرادو" (PDF). p. 5. Retrieved February 19, 2011.
- Arias, E.; Albar, M.; Parra, I; Reza, M. "Regional Definition" (PDF). United Nations Environment Programme. pp. 20–21. Retrieved February 20, 2011.
- "رودخانه کلرادو". Geographic Names Information System (GNIS). United States Geological Survey. February 8, 1980. Retrieved February 4, 2011.
- Derived via Google Earth
- DeLorme (1998). Colorado Atlas and Gazetteer (Map). Section 47–48. ISBN 0-89933-265-X.
- "رود آرکانزاس". Geographic Names Information System (GNIS). United States Geological Survey. November 30, 1979. Retrieved February 4, 2011.
- Benke and Cushing, p. 315
- "Columbia Lake". Natural Resources Canada. Archived from the original on 6 July 2011. Retrieved January 31, 2011.
- "رود کلمبیا". Geographic Names Information System. United States Geological Survey. November 28, 1980. Retrieved August 5, 2010.
- Benke and Cushing, p. 646
- Kleiner, Diana J. "Handbook of تگزاس: Red River". تگزاس State Historical Association. Retrieved February 18, 2011.
- "Handbook of تگزاس: Prairie Dog Town Fork of the Red River". تگزاس State Historical Association. Retrieved February 18, 2011.
- "Handbook of تگزاس: Tierra Blanca Creek". تگزاس State Historical Association. Retrieved February 18, 2011.
- "Red River". Geographic Names Information System (GNIS). United States Geological Survey. June 4, 1980. Retrieved February 5, 2011.
- Benke and Cushing, p. 317
- "Snake River". Geographic Names Information System (GNIS). United States Geological Survey. September 10, 1979. Retrieved August 6, 2010.
- Benke and Cushing, p. 643
- Benke and Cushing, p. 379
- "رود اوهایو". Geographic Names Information System (GNIS). United States Geological Survey. October 24, 1980. Retrieved February 5, 2011.
- Benke and Cushing, p. 413
- Benke and Cushing, p. 198
- "Colorado River". Geographic Names Information System (GNIS). United States Geological Survey. November 30, 1979. Retrieved February 5, 2011.
- Benke and Cushing, p. 222
- Benke and Cushing, p. 384
- "رود تنسی". Geographic Names Information System (GNIS). United States Geological Survey. September 20, 1979. Retrieved February 5, 2011.
- Benke and Cushing, p. 414
- "رود کانادا". Geographic Names Information System (GNIS). United States Geological Survey. December 18, 1979. Retrieved February 5, 2011.
- Benke and Cushing, p. 316
- Benke and Cushing, p. 203
- "رود برازوس". Geographic Names Information System (GNIS). United States Geological Survey. November 30, 1979. Retrieved February 5, 2011.
- Benke and Cushing, p. 223
- Cushing and Benke, p. 497
- "Green River". Geographic Names Information System. United States Geological Survey (USGS). December 31, 1979. Retrieved February 5, 2011.
- Benke and Cushing, p. 528
- Benke and Cushing, p. 213
- "Pecos River". Geographic Names Information System. United States Geological Survey (USGS). November 30, 1979. Retrieved February 5, 2011.
- Benke and Cushing, p. 225
- Benke and Cushing, p. 246
- "White River". Geographic Names Information System. United States Geological Survey (USGS). April 30, 1980. Retrieved February 5, 2011.
- Benke and Cushing, p. 273
- "River Facts". American Rivers. Archived from the original on 10 March 2012. Retrieved February 22, 2011.
- "James River". Geographic Names Information System. United States Geological Survey (USGS). February 13, 1980. Retrieved February 22, 2011.
- "USGS 06478513 James River near Yankton, SD". United States Geological Survey. November 2010. Retrieved February 23, 2011.
- Benke and Cushing, p. 741
- "Kuskokwim River". Geographic Names Information System. United States Geological Survey (USGS). January 1, 2000. Retrieved February 5, 2011.
- Benke and Cushing, p. 764
- "Cimarron River". اکلاهما Historical Society. Archived from the original on 27 December 2014. Retrieved February 5, 2011.
- "Cimarron River". Geographic Names Information System. United States Geological Survey (USGS). December 18, 1979. Retrieved February 5, 2011.
- Benke and Cushing, p. 319
- Benke and Cushing, p. 390
- "Cumberland River". Geographic Names Information System. United States Geological Survey (USGS). September 20, 1979. Retrieved February 5, 2011.
- Benke and Cushing, p. 415
- Benke and Cushing, p. 440
- "Yellowstone River". Geographic Names Information System. United States Geological Survey (USGS). February 13, 1980. Retrieved January 20, 2011.
- Benke and Cushing, p. 470
- Benke and Cushing, p. 451
- "North Platte River". Geographic Names Information System. United States Geological Survey (USGS). October 13, 1978. Retrieved February 6, 2011.
- "Milk River State of the Watershed Report, Part 3" (PDF). Milk River Watershed Council. 2008. Archived from the original (PDF) on 30 September 2018. Retrieved February 19, 2011.
- "Milk River". Geographic Names Information System. United States Geological Survey (USGS). April 4, 1980. Retrieved February 5, 2011.
- Benke and Cushing, p. 475
- Benke and Cushing, p. 265
- "Ouachita River". Geographic Names Information System. United States Geological Survey (USGS). January 1, 2000. Retrieved February 6, 2011.
- Benke and Cushing, p. 279
- Benke and Cushing, p. 987
- "St. Lawrence River (International Section)". U.S. Army Corps of Engineers, Detroit District. Retrieved February 19, 2011.
- "St. Lawrence River". Geographic Names Information System. United States Geological Survey (USGS). January 1, 2000. Retrieved February 3, 2011.
- "Saint Lawrence River". Natural Resources Canada. Archived from the original on 6 July 2011. Retrieved February 3, 2011.
- Benke and Cushing, p. 983
- Benke and Cushing, p. 511
- "Gila River". Geographic Names Information System. United States Geological Survey (USGS). February 8, 1980. Retrieved February 6, 2011.
- Benke and Cushing, p. 531
- McCord, Marc W. "Gila River". Wind Spirit Community. Retrieved February 20, 2011.
- "National Hydrography Dataset". United States Geological Survey. Retrieved June 9, 2011.
- "Sheyenne River". Geographic Names Information System. United States Geological Survey (USGS). February 13, 1980. Retrieved June 9, 2011.
- "Water-Data Report 2010: 05059000 Sheyenne River near Kindred, ND" (PDF). United States Geological Survey. Retrieved June 9, 2011.
- Irwin, Thomas (October 3, 2005). "Recordable Disclaimer of Interest Application for the Nabesna River" (PDF). U.S. Bureau of Land Management. Archived from the original (PDF) on 19 اكتبر 2012. Retrieved February 19, 2011. Check date values in:
|archive-date=(help) - DeLorme (2010). Alaska Atlas and Gazetteer (Map) (7th ed.). p. 98. ISBN 0-89933-289-7.
- "Tanana River". Geographic Names Information System. United States Geological Survey (USGS). January 1, 2000. Retrieved February 2, 2011.
- Benke and Cushing, p. 797
- "Smoky Hill River". Geographic Names Information System. United States Geological Survey (USGS). October 13, 1978. Retrieved June 14, 2011.
- "Water-Data Report 2010: 06877600 Smoky Hill River at Enterprise, KS" (PDF). United States Geological Survey. Retrieved June 14, 2011.
- "Niobrara River". Geographic Names Information System. United States Geological Survey (USGS). March 9, 1979. Retrieved July 5, 2011.
- Benke and Cushing, p. 478
- Personius, Robert Giles; Eddy, Samuel (February 18, 1955). "Fishes of the Little رود میزوری". Copeia. American Society of Icthyologists and Herpetologists. 1955 (1): 41. doi:10.2307/1439450.
- "Little رود میزوری". Geographic Names Information System. United States Geological Survey (USGS). February 13, 1980. Retrieved February 23, 2011.
- "USGS 06337000 Little رود میزوری near Watford City, ND". November 2010. Retrieved February 23, 2011.
- Benke and Cushing, p. 208
- "Sabine River". Geographic Names Information System. United States Geological Survey (USGS). June 4, 1980. Retrieved February 7, 2011.
- Benke and Cushing, p. 224
- "Red River of the North". Minnesota Department of Natural Resources. 2011. Retrieved January 22, 2011.
- "Red River of the North: A Water Trail Guide" (PDF). Minnesota Department of Natural Resources. 2010. Retrieved February 19, 2011.
- "Red River of the North". Geographic Names Information System. United States Geological Survey (USGS). January 1, 2000. Retrieved January 17, 2011.
- "Red River". Natural Resources Canada. Retrieved January 17, 2011.
- Benke and Cushing, p. 896
- "National Recreation Trails: Des Moines River Water Trail - Polk County, آیووا". American Trails. Retrieved February 5, 2011.
- "Des Moines River". Geographic Names Information System. United States Geological Survey (USGS). April 30, 1979. Retrieved February 7, 2011.
- Benke and Cushing, p. 372
- Benke and Cushing, p. 445
- "White River". Geographic Names Information System. United States Geological Survey (USGS). February 13, 1980. Retrieved February 7, 2011.
- Benke and Cushing, p. 471
- Benke and Cushing, p. 215
- "Trinity River". Geographic Names Information System. United States Geological Survey (USGS). November 30, 1979. Retrieved February 7, 2011.
- Benke and Cushing, p. 227
- "رود واباش". Geographic Names Information System. United States Geological Survey (USGS). February 14, 1979. Retrieved July 5, 2011.
- Benke and Cushing, p. 396
- مشارکتکنندگان ویکیپدیا. «List of longest rivers of the United States (by main stem)». در دانشنامهٔ ویکیپدیای انگلیسی، بازبینیشده در ۸ دسامبر ۲۰۱۴.
- Dams, diversions for agriculture, و other human alterations to rivers have greatly affected the discharge of some rivers over time. برای مثال، the virgin discharge of the رودخانه کلرادو is estimated to have been 20,000 ft3/s (566 m3/s) compared to 1,400 ft3/s (~40 m3/s) in 2005.[1]
- Of the total, 10,700 mi2 (28,000 km2), about two percent of the basin, is in Canada.[8][9]
- Kammerer: 76,200 ft3/s (2,160 m3/s).[10]
- Kammerer: 2,340 mi (3,770 km).[10] The Atlas of Canada: 2,348 mi (3,779 km).[8]
- Of the total, 10,700 mi2 (27,800 km2), about two percent of the basin, is in Canada.[8][9]
- Of this total, 714 mi (1,149 km) are in Canada. This amounts to about 36 percent of the main-stem length.[8]
- The Atlas of Canada also lists the total basin size at ۳۲۴٬۰۰۰ mi2 (۸۳۹٬۲۰۰ km2), split between 125,000 mi2 (323,800 km2), about 39 percent, in Canada and 199,000 mi2 (515,400 km2), about 61 percent, in the United States.[8]
- Kammerer: 1,900 mi (3,100 km).[10] University of تگزاس (UT): 1,799 mi (2,895 km).[18] The river forms the U.S. –Mexico border for 1.251 mi (2,013 km) (about 70 percent of its main-stem length) from El Paso to the خلیج مکزیک.[18]
- Rivers of North America says that of this total only about 170,000 mi2 (450,000 km2) of the basin contribute water to the river.[20] The University of تگزاس (UT) says, "The river collects rain, snowmelt and spring water from an area [of] about 215,338 km2 [557,722 km2] including closed basins."[18] It says that 87,020 mi2 (225,380 km2) of the basin (about 48 percent), not counting حوضه بسته، are in Mexico, while 93,821 mi2 (242,994 km2) (about 52 percent) are in the United States.[18] Kammerer cites a total basin size of 336,000 mi2 (۸۷۰٬۰۰۰ km2).[10]
- According to the Utah Division of Water Resources, 75 mi (121 km) of the river are in Mexico. This amounts to about 5 percent of the main-stem length.[21] Of this, 17 mi (27 km) form the border between Mexico and the United States.[22]
- The برنامه محیط زیست ملل متحد cites a total basin size of 246,000 mi2 (637,000 km2), split between 2,000 mi2 (5,200 km2) (about 1 percent) in Mexico and 244,000 mi2 (632,000 km2) (about 99 percent) in the United States.[22]
- Derived by subtracting the length of the East Fork رود آرکانزاس of roughly 16 mi (26 km)[25] from Kammerer's total of 1,459 mi (2,348 km).[10]
- About 498 mi (801 km) are in Canada.[8] This amounts to about 40 percent of the main-stem length.
- The Atlas of Canada lists the total watershed at 259,200 mi2 (671,300 km2), split between 39,700 mi2 (102,800 km2) (about 15 percent) in Canada and 219,500 mi2 (568,500 km2) (about 85 percent) in the United States.[8] Kammerer's figure for the total watershed is 265,000 mi2 (690,000 km2).[10]
- This is the combined length, 1,360 mi (2,190 km),[31] of the main stem, Prairie Dog Town Fork Red River، and Tierra Blanca Creek minus the lengths of the latter two, 160 mi (260 km)[32] and 75 mi (121 km).[33] Kammerer gives the length as 1,290 mi (2,080 km).[10]
- Kammerer: 93,200 mi2.[10]
- Kammerer: 56,000 ft3/s (1,600 m3)[10]
- Also known as the Dakota River or Jim River and not to be confused with the رود جیمز of Virginia.
- This is the average discharge for the years 1982–94, derived by adding the discharge for each of these years and dividing by 13.
- According to the Milk River Watershed Council, a 110-mi (180 km) stretch of the river flows through Canada. This amounts to about 18 percent of the main-stem length.[78]
- The Atlas of Canada: 23,600 mi2 (61,200 km2) split between 8,300 mi2 (21,600 km2) (about 35 percent) in Canada and 15,300 mi2 (39,600 km2) (about 65 percent) in the United States.[8]
- According to the U.S. Army Corps of Engineers، a 115-mi (185 km) stretch of the river forms part of the U.S. –Canada border. This amounts to about 19 percent of the main-stem length.[85]
- Kammerer: 396,000 mi2 (1,030,000 km2).[10] The Atlas of Canada: 519,000 mi2 (1,344,200 km2), of which 324,000 mi2 (839,200 km2) (about 62 percent) is in Canada and 195,000 mi2 (505,000 km2) (about 38 percent) is in the United States.[8]
- Kammerer: 348,000 ft3/s (9,900 m3/s).[10]
- Of this total, 232 mi2 (600 km2) (about 0.4 percent) are in the Mexican state of سونورا، and the rest is in the United States.[92]
- Rivers of North America describes the discharge as less than 210 ft3/s (6 m3/s.
- This is the size of the basin upstream of a ایستگاه هیدرومتری near Kindred and at رود مایل 67.9 (river kilometer 109.3).[95]
- This is the average flow measured by a ایستگاه هیدرومتری near Kindred and at رود مایل 67.9 (river kilometer 109.3).[95]
- The main-stem length is calculated by subtracting the length of the Nabesna River from Kammerer's total of 659 mi (1,061 km).[10] The Nabesna River is roughly 75 mi (121 km) long, calculated by adding the 60 mi (97 km) from the Nabesna mouth to Camp Creek[96] to the distance, 15 mi (24 km), from Camp Creek to Nabesna Glacier,[97] Kammerer's most remote source for the Tanana.
- Reflects only that part of the basin above a ایستگاه هیدرومتری at رود مایل 43.3 (river kilometer 69.7) near Enterprise.[101]
- Measured by a ایستگاه هیدرومتری at رود مایل 43.3 (river kilometer 69.7) near Enterprise.[101]
- This is only a close approximation of the entire basin. It does not include a small fraction of the basin below the river gauge, located about 25 mi (40 km) upstream of the river mouth.
- This is the average discharge for the years 1990–2010, derived by adding the discharge for each of these years and dividing by 21.
- According to the Minnesota Department of Natural Resources، 394 mi (634 km) are in the United States. This amounts to about 72 percent of the main-stem length.[111]
- Of the total basin, 53,500 mi2 (138,600 km2) (about 48 percent) are in Canada and 57,500 mi2 (148,900 km2) (about 52 percent) are in the United States.[8]
This article is issued from Wikipedia. The text is licensed under Creative Commons - Attribution - Sharealike. Additional terms may apply for the media files.

































