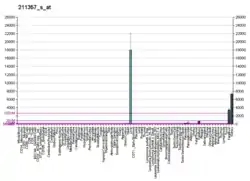
آلدولاز B
آلدولاز B (انگلیسی: Aldolase B) که با نام فروکتوز-بیسفسفات B و آلدولاز کبدی هم شناخته میشود یک آنزیم است که در انسان توسط ژن «ALDOB» واقع بر کروموزوم ۹ کُدگذاری میشود. این پروتئین یکی از آنزیمهای گلیکولیز است که واکنش برگشتپذیر تبدیل فروکتوز ۱-فسفات را به دیهیدروکسیاستون فسفات و گلیسرآلدئید کاتالیزه میکند. در پستانداران آلدولاز B، آلدولاز A در ماهیچهها و آلدولاز C در مغز بیان میشود. ژن مذکور، ۱۴٬۵۰۰ جفتباز دراز داشته و حاوی ۹ اگزون است.[1][2][3]
| Aldolase, fructose-bisphosphate B | |||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
 | |||||||||||||||
| معینکنندهها | |||||||||||||||
| نامهای دیگر | ALDOBaldolase Bfructose-bisphosphatasealdolase 2fructose-bisphosphate aldolase Bliver-type aldolasealdolase Bfructose-bisphosphate | ||||||||||||||
| شناسههای بیرونی | GeneCards: | ||||||||||||||
| |||||||||||||||
| همساختشناسی | |||||||||||||||
| گونهها | انسان | موش | |||||||||||||
| Entrez |
|
| |||||||||||||
| آنسامبل |
|
| |||||||||||||
| یونیپروت |
|
| |||||||||||||
| RefSeq (mRNA) |
|
| |||||||||||||
| RefSeq (پروتئین) |
|
| |||||||||||||
| موقعیت (UCSC) | n/a | n/a | |||||||||||||
| جستجوی PubMed | n/a | n/a | |||||||||||||
| ویکیداده | |||||||||||||||
| |||||||||||||||
آلدولاز B ترجیح خاصی برای فروکتوز ۶٬۱-بیسفسفات یا فروکتوز ۱-فسفات ندارد، حال آنکه آلدولاز A و آلدولاز C، فروکتوز ۶٬۱-بیسفسفات را ترجیح میدهند.[4]
اهمیت بالینی
نقص در این آنزیم با بروز بیماری عدم تحمل ارثی فروکتوز (HFI)[5] که یک بیماری ژنتیکی اتوزومال مغلوب است، مرتبط بوده و در حدود ۳۰ جهش ژنی در ارتباط با این بیماری کشف شدهاست. مجموعهای از این جهشهای ژنی باعث میشود که میزان بروز عدم تحمل ارثی فروکتوز در حدود ۱ مورد از ۲۰٬۰۰۰ تولد باشد.[6][7]
منابع
- "Entrez Gene: ALDOB aldolase B, fructose-bisphosphate".
- Henry I, Gallano P, Besmond C, Weil D, Mattei MG, Turleau C, Boué J, Kahn A, Junien C (July 1985). "The structural gene for aldolase B (ALDB) maps to 9q13----32". Ann. Hum. Genet. 49 (Pt 3): 173–80. doi:10.1111/j.1469-1809.1985.tb01691.x. PMID 3000275.
- Tolan DR, Penhoet EE (June 1986). "Characterization of the human aldolase B gene". Mol. Biol. Med. 3 (3): 245–64. PMID 3016456.
- Dalby AR, Tolan DR, Littlechild JA (November 2001). "The structure of human liver fructose-1,6-bisphosphate aldolase". Acta Crystallogr. D. 57 (Pt 11): 1526–33. doi:10.1107/S0907444901012719. PMID 11679716.
- Cox TM (January 1994). "Aldolase B and fructose intolerance". FASEB J. 8 (1): 62–71. PMID 8299892.
- Esposito G, Vitagliano L, Santamaria R, Viola A, Zagari A, Salvatore F (November 2002). "Structural and functional analysis of aldolase B mutants related to hereditary fructose intolerance". FEBS Lett. 531 (2): 152–6. doi:10.1016/S0014-5793(02)03451-8. PMID 12417303.
- Inborn Metabolic Diseases (Fourth Revised ed.). Springer Berlin Heidelberg. 2006.
- مشارکتکنندگان ویکیپدیا. «Aldolase B». در دانشنامهٔ ویکیپدیای انگلیسی، بازبینیشده در ۲۱ اکتبر ۲۰۱۸.
بیشتر بخوانید
- Cross NC, de Franchis R, Sebastio G, et al. (1990). "Molecular analysis of aldolase B genes in hereditary fructose intolerance". Lancet. 335 (8685): 306–9. doi:10.1016/0140-6736(90)90603-3. PMID 1967768.
- Cross NC, Stojanov LM, Cox TM (1990). "A new aldolase B variant, N334K, is a common cause of hereditary fructose intolerance in Yugoslavia". Nucleic Acids Res. 18 (7): 1925. doi:10.1093/nar/18.7.1925. PMC 330648. PMID 2336380.
- Sakakibara M, Mukai T, Yatsuki H, Hori K (1985). "Human aldolase isozyme gene: the structure of multispecies aldolase B mRNAs". Nucleic Acids Res. 13 (14): 5055–69. doi:10.1093/nar/13.14.5055. PMC 321849. PMID 2410860.
- Sakakibara M, Takahashi I, Takasaki Y, et al. (1989). "Construction and expression of human aldolase A and B expression plasmids in Escherichia coli host". Biochim. Biophys. Acta. 1007 (3): 334–42. doi:10.1016/0167-4781(89)90156-5. PMID 2649152.
- Mukai T, Yatsuki H, Arai Y, et al. (1988). "Human aldolase B gene: characterization of the genomic aldolase B gene and analysis of sequences required for multiple polyadenylations". J. Biochem. 102 (5): 1043–51. PMID 2830249.
- Cross NC, Tolan DR, Cox TM (1988). "Catalytic deficiency of human aldolase B in hereditary fructose intolerance caused by a common missense mutation". Cell. 53 (6): 881–5. doi:10.1016/S0092-8674(88)90349-2. PMID 3383242.
- Paolella G, Santamaria R, Izzo P, et al. (1984). "Isolation and nucleotide sequence of a full-length cDNA coding for aldolase B from human liver". Nucleic Acids Res. 12 (19): 7401–10. doi:10.1093/nar/12.19.7401. PMC 320170. PMID 6548561.
- Rottmann WH, Tolan DR, Penhoet EE (1984). "Complete amino acid sequence for human aldolase B derived from cDNA and genomic clones". Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. U.S.A. 81 (9): 2738–42. doi:10.1073/pnas.81.9.2738. PMC 345145. PMID 6585824.
- Besmond C, Dreyfus JC, Gregori C, et al. (1984). "Nucleotide sequence of a cDNA clone for human aldolase B". Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 117 (2): 601–9. doi:10.1016/0006-291X(83)91243-3. PMID 6689266.
- Ali M, Cox TM (1995). "Diverse mutations in the aldolase B gene that underlie the prevalence of hereditary fructose intolerance". Am. J. Hum. Genet. 56 (4): 1002–5. PMC 1801191. PMID 7717389.
- Ali M, Sebastio G, Cox TM (1994). "Identification of a novel mutation (Leu 256→Pro) in the human aldolase B gene associated with hereditary fructose intolerance". Hum. Mol. Genet. 3 (1): 203–4. doi:10.1093/hmg/3.1.203. PMID 8162030.
- Brooks CC, Tolan DR (1994). "A partially active mutant aldolase B from a patient with hereditary fructose intolerance". FASEB J. 8 (1): 107–13. PMID 8299883.
- Kusakabe T, Motoki K, Hori K (1997). "Mode of interactions of human aldolase isozymes with cytoskeletons". Arch. Biochem. Biophys. 344 (1): 184–93. doi:10.1006/abbi.1997.0204. PMID 9244396.
- Lau J, Tolan DR (1999). "Screening for hereditary fructose intolerance mutations by reverse dot-blot". Mol. Cell. Probes. 13 (1): 35–40. doi:10.1006/mcpr.1998.0208. PMID 10024431.
- Santamaria R, Esposito G, Vitagliano L, et al. (2001). "Functional and molecular modelling studies of two hereditary fructose intolerance-causing mutations at arginine 303 in human liver aldolase". Biochem. J. 350 Pt 3 (Pt 3): 823–8. doi:10.1042/0264-6021:3500823. PMC 1221316. PMID 10970798.
- Susan PP, Dunn WA (2001). "Starvation-induced lysosomal degradation of aldolase B requires glutamine 111 in a signal sequence for chaperone-mediated transport". J. Cell. Physiol. 187 (1): 48–58. doi:10.1002/1097-4652(2001)9999:9999<00::AID-JCP1050>3.0.CO;2-I. PMID 11241348.
پیوند به بیرون
- Aldolase B در سرعنوانهای موضوعی پزشکی (MeSH) در کتابخانهٔ ملی پزشکی ایالات متحدهٔ آمریکا
- مکان ژنوم ALDOB انسانی و صفحهٔ جزئیات ژنی ALDOB در سامانه جستجوی بانک ژنی دانشگاه کالیفرنیا، سانتا کروز.