حالت ماده
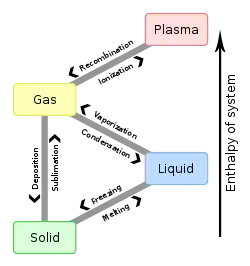
در فیزیک، حالت ماده (State of matter)، یکی از چهار حالت متمایز ماده است که فقط در اثر تغییر دما یا فشار، قابل تبدیل به یکدیگر هستند. در زندگی روزمره، ۴ حالت ماده قابل مشاهدهاند: جامد، مایع، گاز و پلاسما

حالتهای چهارگانه ماده
البته ماده، حالتهای دیگری مانند چگالش بوز-اینشتین و چگالی فرمیونی هم دارد؛ اما این حالتها تنها در شرایط خاصی مشاهده میشوند.
حالت ماده را نباید با فاز ماده یکی دانست.
جستارهای وابسته
- چگالی فرمیونی
- چگالش بوز-اینشتین
- پلاسما
- فاز ماده
منابع
- It is often stated that more than 99% of the material in the visible universe is plasma. See, for example, D. A. Gurnett, A. Bhattacharjee (2005). Introduction to Plasma Physics: With Space and Laboratory Applications. Cambridge, UK: Cambridge University Press. p. 2. ISBN 0-521-36483-3. and K Scherer, H Fichtner, B Heber (2005). Space Weather: The Physics Behind a Slogan. Berlin: Springer. p. 138. ISBN 3-540-22907-8.. Essentially, all of the visible light from space comes from stars, which are plasmas with a temperature such that they radiate strongly at visible wavelengths. Most of the ordinary (or baryonic) matter in the universe, however, is found in the Outer space, which is also a plasma, but much hotter, so that it radiates primarily as X-rays. The current scientific consensus is that about 96% of the total energy density in the universe is not plasma or any other form of ordinary matter, but a combination of cold dark matter and dark energy.
This article is issued from Wikipedia. The text is licensed under Creative Commons - Attribution - Sharealike. Additional terms may apply for the media files.