دمکلوسایکلین
دمکلوسایکلین (INN , BAN , USAN) (تحت نامهای تجاری Declomycin , Declostatin , Ledermycin , Bioterciclin , Deganol , Deteclo ) و همچنین با نامهای تجاریDetravis , Meciclin ,Mexocine ,Clortetrin نیز شناخته میشود، یک آنتی بیوتیک از دسته تتراسایکلینها است که از یک سویه جهش یافته از Streptomyces aureofaciens به دست میآید.[1][2]
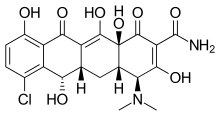 | |
| نامگذاری آیوپاک | |
|---|---|
(2E,4S,4aS,5aS,6S,12aS)-2-[amino(hydroxy)methylidene]-7-chloro-4-(dimethylamino)-6,10,11,12a-tetrahydroxy-1,2,3,4,4a,5,5a,6,12,12a-decahydrotetracene-1,3,12-trione | |
| اطلاعات درمانی | |
| نام تجاری | Declomycin |
| AHFS/دراگز | monograph |
| مدلاین پلاس | a682103 |
| ردهٔ بارداری |
|
| وضعیت قانونی |
|
| روش مصرف دارو | خوراکی |
| اطلاعات فارماکوکینتیک | |
| فراهمی زیستی | ۶۰–۸۰٪ |
| پیوند پروتئینی | ۴۱–۵۰٪ |
| سوخت و ساز | کبد |
| نیمهعمر (داروشناسی) | ۱۰–۱۷ ساعت |
| دفع | کلیه |
| شناسهها | |
| سیایاس | ۱۲۷-۳۳-۳ 64-73-3 (HCl) |
| ایتیسی | D06AA01 J01AA01 (WHO) |
| پابکم | CID: ۵۴۶۸۰۶۹۰ |
| دراگبنک | DB00618 |
| کماسپایدر | ۱۰۴۸۲۱۱۷ |
| UNII | 5R5W9ICI6O |
| KEGG | D03680 |
| ChEBI | CHEBI:۴۳۹۲ |
| ChEMBL | CHEMBL۱۵۹۱ |
| مترادفs | RP-10192 |
| اطلاعات شیمیایی | |
| فرمول شیمیایی | C۲۱H۲۱Cl۱N۲O۸ |
| وزن مولکولی | خطای عبارت: عملگر < دور از انتظار |
| |
| (بررسی) | |
دمکلوسایکلین به طور رسمی برای درمان انواع عفونتهای باکتریایی مورد استفاده قرار میگیرد.[3] از آن به عنوان یک آنتی بیوتیک در درمان بیماری لایم، [4] آکنه، [5] و برونشیت استفاده میشود.[6] اگرچه مقاومت به آن تدریجاً شایع میشود، [7] و این دارو اکنون به ندرت برای درمان عفونتها استفاده میشود. [8] [9]
منابع
- Chopra, I.; Hawkey, P. M.; Hinton, M. (1992). "Tetracyclines, molecular and clinical aspects". J. Antimicrob. Chemother. 29 (3): 245–277. doi:10.1093/jac/29.3.245.
- J. Elks (14 November 2014). The Dictionary of Drugs: Chemical Data: Chemical Data, Structures and Bibliographies. Springer. pp. 356–. ISBN 978-1-4757-2085-3.
- DailyMed. "Demeclocycline Hydrochloride - demeclocycline tablet". Drug label information. Retrieved 2008-12-20.
- Rosner, Bryan (2007). The Top 10 Lyme Disease Treatments: Defeat Lyme Disease with the Best of Conventional and Alternative Medicine. pp. 84, 86.
- Ad Hoc Committee on the Use of Antibiotics in Dermatology (1975). "Systemic antibiotics for treatment of acne vulgaris: efficacy and safety". Arch. Dermatol. 111 (12): 1630–1636. doi:10.1001/archderm.1975.01630240086015. PMID 128326.
- Beatson, J. M.; Marsh, B. T.; Talbot, D. J. (1985). "A clinical comparison of pivmecillinam plus pivampicillin (Miraxid) and a triple tetracycline combination (Deteclo) in respiratory infections treated in general practice". J. Int. Med. Res. 13 (4): 197–202. doi:10.1177/030006058501300401.
- Schnappinger, Dirk; Hillen, Wolfgang (July 1996). "Tetracyclines: Antibiotic action, uptake, and resistance mechanisms". Archives of Microbiology. 165 (6): 359–369. doi:10.1007/s002030050339.
- Klein, Natalie C.; Cunha, Burke A. (1995). "Tetracyclines". Medical Clinics of North America. 79 (4): 789–801. doi:10.1016/S0025-7125(16)30039-6.
- Lexi-Comp (August 2008). "Demeclocycline". The Merck Manual Professional. Retrieved on October 27, 2008.
This article is issued from Wikipedia. The text is licensed under Creative Commons - Attribution - Sharealike. Additional terms may apply for the media files.